Introduction to Ice Cream Nutrition: Ice Cream Nutrition Facts
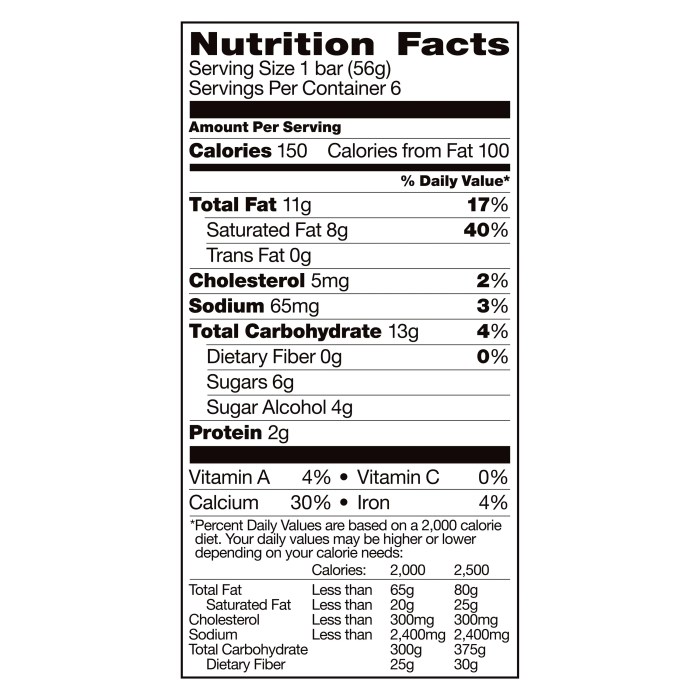
Ice cream nutrition facts – Ice cream, a beloved frozen dessert enjoyed worldwide, presents a complex nutritional profile that varies significantly depending on its ingredients and manufacturing process. Understanding this profile is crucial for making informed choices about consumption, particularly considering its often high calorie, fat, and sugar content. This section will explore the nutritional composition of different ice cream types and provide a comparative analysis of popular brands.Ice cream’s nutritional makeup primarily consists of fat, sugar, and protein, with varying amounts of carbohydrates and minerals depending on the specific recipe.
Dairy-based ice creams, the most common type, derive their richness from milkfat and added cream. These contribute significantly to the overall calorie and fat content. Non-dairy ice creams, increasingly popular among those with lactose intolerance or vegan preferences, often utilize plant-based milks like almond, soy, or coconut milk, resulting in different fat and protein profiles. Low-fat ice creams aim to reduce calorie and fat intake by using skimmed milk or reduced-fat alternatives; however, this often leads to an increase in added sugars to maintain flavor and texture.
Nutritional Comparison of Ice Cream Types
The table below illustrates the variability in calorie, fat, and sugar content across different ice cream types and brands. Note that these values are approximate and can vary depending on serving size and specific product variations. Always refer to the individual product packaging for the most accurate nutritional information.
| Brand | Type | Calories (per serving) | Fat (grams per serving) | Sugar (grams per serving) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | Dairy, Full-Fat | 250 | 14 | 26 |
| Brand B | Dairy, Low-Fat | 180 | 6 | 28 |
| Brand C | Non-Dairy (Almond) | 200 | 10 | 22 |
| Brand D | Dairy, Light | 150 | 4 | 20 |
Ice Cream and Dietary Considerations
Ice cream, while undeniably delicious, presents a unique challenge within a balanced diet. Its high sugar and fat content necessitates mindful consumption to prevent negative impacts on overall health. Understanding its nutritional profile and how it fits into various dietary approaches is key to enjoying ice cream responsibly.Ice cream’s role in a balanced diet is primarily one of occasional indulgence, not a staple food group.
It can contribute to overall caloric intake and provide some micronutrients depending on the specific ingredients, but should not be relied upon as a significant source of essential vitamins or minerals. A balanced diet focuses on whole, unprocessed foods, and ice cream, due to its processed nature and typically high sugar content, should be consumed sparingly.
Dietary Recommendations for Ice Cream Consumption
The key to incorporating ice cream into a healthy eating plan lies in portion control and frequency. Overconsumption can lead to weight gain, blood sugar spikes, and other health issues. Consider these guidelines:
- Portion Size: Opt for smaller servings (e.g., a half-cup) rather than larger portions. This helps manage calorie intake and sugar consumption.
- Frequency: Limit ice cream consumption to a few times per week, or even less frequently, depending on individual dietary needs and goals. Treating it as an occasional treat rather than a regular part of the diet is crucial.
- Ingredient Awareness: Choose ice cream with lower added sugar content and higher quality ingredients. Look for brands that prioritize real fruit and less processed ingredients.
Ice Cream and Various Dietary Plans, Ice cream nutrition facts
Ice cream’s compatibility with different dietary plans varies greatly. Understanding the nutritional makeup of different ice cream options is critical for making informed choices.
Understanding ice cream nutrition facts requires careful consideration of serving sizes and ingredients. For a contrasting example of a high-calorie, customizable meal, you might compare the nutritional information to something like a chipotle burrito bowl nutrition facts , which often features significant amounts of rice, beans, and meat. Returning to ice cream, the fat and sugar content are key factors to watch when assessing its overall nutritional value.
Ice Cream in Vegan Diets
Many vegan ice cream options are available, utilizing plant-based milks (like almond, soy, or coconut milk) and other plant-derived ingredients to mimic the creamy texture of traditional ice cream. However, it’s important to check labels for added sugars and other potential allergens. For example, many coconut-based ice creams are high in saturated fat, so moderation remains key.
Ice Cream in Keto and Low-Carb Diets
The high sugar content of most ice creams makes them generally unsuitable for ketogenic or low-carb diets. However, some specialized brands offer keto-friendly ice cream options using sugar substitutes and low-carb sweeteners. These often rely on ingredients like erythritol or stevia, and their impact on individual metabolic responses can vary. Always check the nutritional label for carbohydrate content to ensure it aligns with your dietary plan.
A serving of a low-carb ice cream might contain 5-10 grams of net carbs per serving compared to traditional ice cream with 20-30 grams.
Health Implications of Ice Cream Consumption

Ice cream, while undeniably delicious, presents a complex relationship with health. Moderate consumption is generally acceptable for most individuals, but excessive indulgence can contribute to various health concerns. Understanding the potential risks and making informed choices about ice cream consumption is key to maintaining a balanced diet.Excessive ice cream consumption is primarily linked to weight gain due to its high calorie and fat content.
Many commercially available ice creams are loaded with added sugars, further exacerbating this issue and potentially leading to blood sugar spikes and insulin resistance, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes. The type of fat present also matters; high saturated and trans fat content contributes to elevated cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Impact of Ice Cream Ingredients on Overall Health
The nutritional profile of ice cream varies significantly depending on its ingredients. High-sugar ice creams contribute to weight gain, tooth decay, and energy crashes. Ice creams high in saturated fat can negatively impact cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. Conversely, ice creams containing fruits and nuts offer added nutritional benefits like vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
The presence of dairy provides calcium and protein, contributing to bone health and satiety. However, individuals with lactose intolerance should exercise caution.
Healthier Ice Cream Alternatives and Their Nutritional Benefits
Fortunately, healthier alternatives exist for those seeking to enjoy the pleasures of ice cream without the significant health drawbacks. Frozen yogurt, for example, often contains less fat and sugar than traditional ice cream while offering probiotics beneficial for gut health. Sorbet, made primarily from fruit and sugar, is naturally lower in fat and calories, though it might be higher in sugar depending on the recipe.
Homemade ice cream allows for precise control over ingredients, enabling the incorporation of healthier options such as fruit purees, less sugar, and alternatives to dairy such as coconut milk or almond milk, leading to a reduction in saturated fat and potential lactose issues. These alternatives provide a broader range of nutritional benefits, including increased fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, depending on the chosen ingredients.
For example, a homemade ice cream using berries and coconut milk will offer a good source of antioxidants and healthy fats, compared to a standard high-sugar, high-fat commercial option.
FAQs
Is ice cream a good source of calcium?
Dairy-based ice creams can be a good source of calcium, but the amount varies depending on the brand and ingredients. Non-dairy options generally contain less or no calcium.
Does ice cream contain any fiber?
Ice cream typically contains minimal fiber. Some brands might incorporate ingredients that slightly increase fiber content, but it’s generally not a significant source.
Are there ice cream options suitable for people with lactose intolerance?
Yes, many non-dairy ice cream options are available, using ingredients like almond milk, soy milk, or coconut milk, making them suitable for those with lactose intolerance.
How can I reduce the sugar content in my ice cream consumption?
Choose low-sugar or no-sugar-added ice cream brands. You can also opt for sorbets or frozen yogurt, which naturally contain less sugar than traditional ice cream.
